Trending Bit
Translate
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Determination of the equivalent resistance of two resistors are connected in parallel combination
PARALLEL COMBINATION OF RESISTORS
When two or more resistors are joined or connected if one of each resistance is connected to 1 point and the other is connected to another point is known as a parallel combination. In this combination, the voltage (potential difference) across each resistor is the same, and the current where is across the resistors. In this experiment, the current is made to flow between resistors connected in parallel combination.
Aim of the experiment :
To determine the equivalent resistance of the two resistors when connected in parallel combination. OR to verify the law of combination of resistance in parallel combination.
Apparatus required :
- Meter bridge
- Two resistors of different values
- Galvanometer
- Plug Key
- Battery
- Jockey
- Connecting wires
Principle of the experiment :
01. Wheatstone's bridge is balanced when the current through the galvanometer is zero.
02. If P, Q, R & S represent the resistances of four arms of Wheatstone's bridge. Then, P/Q = R/S
Formula :
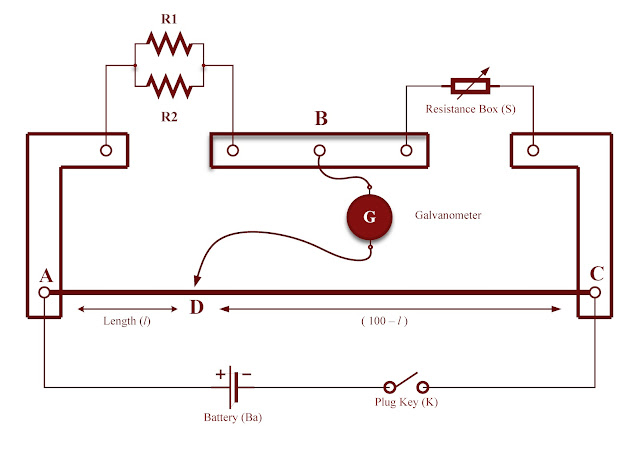
Circuit diagram :
Procedure :
- The connections are made as shown in the circuit diagram respectively.
- A suitable standard resistance S is unplugged into the resistance box.
- The circuit is checked for opposite deflections by placing the Jockey at the two ends of the meter bridge wire AC alternatively.
- The Jockey is moved on the wire from end A towards C till the galvanometer shows zero deflection.
- The balancing length, l is measured. The equivalent resistance of the parallel combination is calculated using the formula. Rp = Sl/(100 -l)
- The experiment is repeated for different values of S and the average value of Rp is calculated.
Observation :
01. Resistance, R1 = ................................Ω
02. Resistance, R2 = ................................Ω
Tabular column :
| Trial No | Resistance, S in (Ω Ohm) | Balencing length, l in (cm) | (100 - l) in (cm) | Resistance, Rp = Sl/(100 - l) in (Ω Ohm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01. | ||||
| 02. | ||||
| 03. | ||||
| 04. | ||||
| 05. | ||||
| Mean Rp = ...........Ω |
||||
Calculations :
01. Theoretical value of equivalent resistance, Rp = R1*R2 / R1 + R2 = ................................Ω
Result :
The theoretical value of resistance Rp = ...............Ω is nearly equal to the experimental value of resistance Rp = ...............Ω. Hence the law of combination of resistances in series is verified.
BITS ARROW
Popular Posts
To determine the resistance of the given wire using a metre bridge and hence to find the resistivity of the material
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
To convert the given galvanometer of known resistance and figure of merit into a voltmeter of desired range and to verify the same
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
How to change the capitalization or cases of selected texts in Microsoft word
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
To compare the EMF's of given two primary cells using a potentiometer
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
List of complete Physics practical experiments for 2nd PU students
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
List of complete Physics practical Viva-Voce questions with answers for 2nd PU students
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps





Comments
Post a Comment