Trending Bit
Translate
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
To convert the given galvanometer of known resistance and figure of merit into an ammeter of desired range and verify the same
CONVERSION OF GALVANOMETER INTO AMMETER
A galvanometer is an electronic device that is used to detect mild currents in an electrical circuit. In order to measure large currents it is converted into an Ammeter by connecting a low resistance called as shunt resistance in parallel to the galvanometer. Hence, we will consider it as the conversion of a galvanometer into an ammeter.
Aim of the experiment :
To convert the given galvanometer into an ammeter of the required range (0-30mA) and verify the same.
Apparatus required :
- Connecting wires
- Galvanometer
- Battery
- Rheostat
- Plug Key
- Ammeter
- Resistor
Principle of the experiment :
Galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter by connecting a suitable low resistance in parallel with it, so that very small current flows through the galvanometer.
Formula :
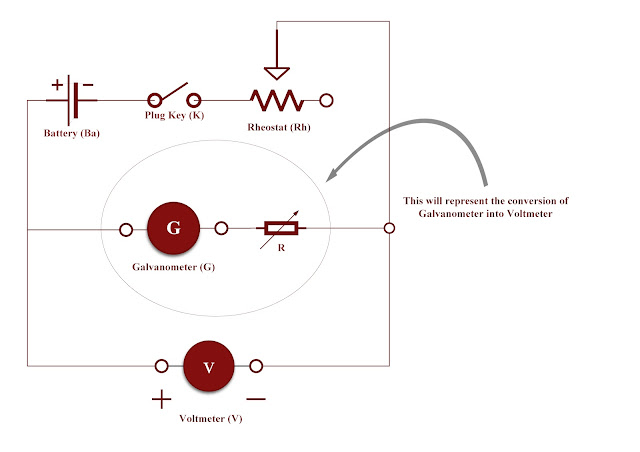
Circuit diagram :
The circuit diagram for the conversion of the galvanometer into an ammeter is as follows below.
 |
| To convert the given galvanometer into ammeter |
Procedure :
- The current for the full-scale deflection in the galvanometer, Ig = N*K is calculated.
- The shunt resistance S is calculated using the formula S = Ig*G/I-Ig
- With the given values of radius,r and resistivity, ρ f the wire, the length, l of the wire is calculated using the formula as follows l = Sπr2/ρ
- The wire of a slightly longer length than the calculated length is connected in parallel with the galvanometer and connections are made as shown in the circuit diagram respectively.
- The rheostat is adjusted for 30mA current in the ammeter.
- The length of the wire is adjusted for full-scale deflection in the galvanometer and its length l is measured.
- Shunt resistance S is calculated using the formula, S' = ρl'/πr2
- S' is equal or nearly equal to S and hence conversion is verified.
Observation :
- Resistance of the galvanometer, G (given) = ..................................Ω ohm.
- Figure of merit of the galvanometer, K (given) = ..................................A/div.
- Number of divisions on either side of zero of the galvanometer scale, N = ..................................A.
- Current required for producing full-scale deflection of N divisions, Ig = N*K = ..................................Ampere
- Maximum current to be measured, I (say 30mA) = ..................................Ampere.
Calculation :
Shunt resistance , S = Ig*G/I-Ig =.................................. (in Ω ohm)
Result :
01. The theoretical value of shunt resistance, S =..................................(in Ω ohm)
02. The experimental value of shunt resistance, S' =..................................(in Ω ohm)
BITS ARROW
Popular Posts
To determine the resistance of the given wire using a metre bridge and hence to find the resistivity of the material
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
To convert the given galvanometer of known resistance and figure of merit into a voltmeter of desired range and to verify the same
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
How to change the capitalization or cases of selected texts in Microsoft word
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
To compare the EMF's of given two primary cells using a potentiometer
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
List of complete Physics practical experiments for 2nd PU students
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
List of complete Physics practical Viva-Voce questions with answers for 2nd PU students
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps





Comments
Post a Comment