Trending Bit
Translate
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
To convert the given galvanometer of known resistance and figure of merit into a voltmeter of desired range and to verify the same
CONVERSION OF GALVANOMETER INTO VOLTMETER
A galvanometer is an electronic device that is used to detect mild currents in an electrical circuit. Galvanometer works on the principle of a coil placed in a uniform magnetic field that experiences a torque when an electric current is set up in it We can convert a galvanometer into a voltmeter by connecting a large resistance in series to the galvanometer.
Aim of the experiment :
To convert the given galvanometer into a voltmeter of the required range (0 - 3V) and verify the same.
Apparatus required :
- Connecting wire
- Galvanometer
- Battery
- Voltmeter
- Resistance box
- Plug Key
- Rheostat
Principle of the experiment :
Galvanometer can be converted into a voltmeter by connecting suitable high resistance in series with it so that a very small current flows through the galvanometer
Formula :
Circuit diagram :
The circuit diagram for converting the given galvanometer of known resistance and figure of merit into a voltmeter is as follows below :
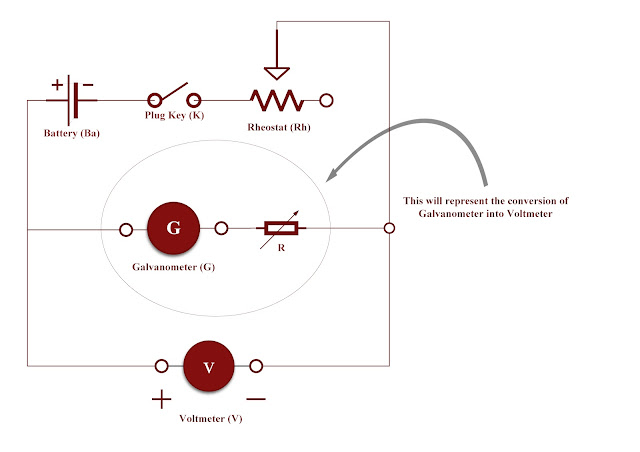 |
| Conversion of Galvanometer into voltmeter |
Procedure :
- The value of resistance is calculated using the formula, R = V / Ig - G
- The circuit connections are made as shown in the circuit diagram.
- The calculated high resistance, R is unplugged in the standard resistance box and the rheostat is adjusted so that the voltage shown in the voltmeter is equal to the desired range (say 3V).
- Resistance from the resistance box is adjusted such that the galvanometer shows full-scale deflection. Then R' from the resistance box is noted.
- P' is equal or nearly equal to R. Hence conversion is verified.
Observation :
- Resistance of the galvanometer, G (given) = ..................................Ω ohm.
- Figure of merit of the galvanometer, K (given) = ..................................A/div.
- Number of divisions on either side of zero of the galvanometer scale, N = ..................................A.
- Current required for producing full-scale deflection of N divisions, Ig = N*K = ..................................Ampere
- Maximum voltage to be measured, V (say 3V) = ..................................V.
Calculation :
High resistance to be connected in series with the galvanometer, R = V / Ig - G
Result :
01. The value of the theoretically calculated value of series resistance, R = ..................................Ω ohm.
02. Practically observed value of series resistance, R' = ..................................Ω ohm.
Note :
High resistance of order of 10K should be unplugged in the resistance box first and then key has to be closed to avoid any damage to the galvanometer.
BITS ARROW
Popular Posts
How to change the capitalization or cases of selected texts in Microsoft word
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
To determine the resistance of the given wire using a metre bridge and hence to find the resistivity of the material
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
To determine the resistance of a galvanometer by half deflection method and to find its figure of merit of galvanometer
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
To compare the EMF's of given two primary cells using a potentiometer
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
How to enroll students through Transfer Certificate (Higher Standard) in SATS Portal (Student Achievement Tracking System)
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps




Comments
Post a Comment